The FreeCAD interface
FreeCAD uses the Qt framework) to draw and manage its interface. This framework is used in a wide range of applications, so the FreeCAD interface is very classical and presents no particular difficulty to understand. Most buttons are standard and will be found where you expect them (File -> Open, Edit -> Paste, etc). Here is the look of FreeCAD when you open it for the first time, just after installing, showing you the start center:

The start center is a convenient "welcome screen", that shows useful information for newcomers, like the latest files you have been working on, what's new in the FreeCAD world, or quick info about the most common Workbenches. It will also notify you if a new stable version of FreeCAD is available.
Close the Start Page tab (click on the tab x near the bottom) and create a new document (Ctrl-N):

Workbenches
Note that some of the icons have changed between the two screencaptures above. This is where the most important concept used in the FreeCAD interface comes into play: Workbenches.
Workbenches are group of tools (toolbar buttons, menus, and other interface controls) that are grouped together by specialty. Think of a workshop where you have different people working together: A person who works with metal, another with wood. Each of them has, in their workshop, a separate table with specific tools for his/her job. However, they can all work on the same objects. The same happens in FreeCAD.
The most important control of the FreeCAD interface is the Workbench selector, which you use to switch from one Workbench to another:

Workbenches often confuse new users, since it's not always easy to know in which Workbench to look for a specific tool. But they are quick to learn, and after a short while, they will feel natural. New users quickly realize Workbenches are a convenient way to organize the multitude of tools FreeCAD has to offer. In addition, Workbenches are also fully customizable (see below).
Later in this manual, you will find a table showing typical Workbench contents.
The interface
Let's have a better look at the different parts of the interface:

- The 3D view is the main component of the interface. It can be undocked out of the main window, you can have several views of the same document (or same objects), or several documents opened at the same time. You can select objects or parts of objects by clicking them, and you can pan, zoom and rotate the view with the mouse buttons. This will be explained further in the next chapter.
- The combo view on the left side of the window, has two tabs:
- The Model tab shows you the contents and structure of your document (see above) and the properties (or parameters) of the selected object(s) (see below.) These Model Tab properties are separated in two categories:
- Data (properties which concern the geometry itself)
- View (properties that affect how the geometry looks like on screen).
- The Tasks tab is where FreeCAD will prompt you for values specific to the tool you're currently using at the time—for example, entering a 'length' value when the Line tool is being used. It will close automatically after pressing the OK (or Cancel) button. Also, by double-clicking the related object in the combo view, most tools will allow you to reopen that task panel in order to modify the settings.
- The Model tab shows you the contents and structure of your document (see above) and the properties (or parameters) of the selected object(s) (see below.) These Model Tab properties are separated in two categories:
- The report view is normally hidden, but it is a good idea to leave open as it will list any information, warnings or errors to help you decipher (or debug) what you may have done wrong. (View menu -> Panels -> Report View checked)
- The Python console is also hidden by default. This is where you can interact with the contents of the document using the Python language. Since every action you do on the FreeCAD interface actually executes a piece of Python code, having this open allows you to watch the code unfold in real time—allowing you a wonderful and easy way to learn a little Python on the way, almost without noticing it. (View menu -> Panels -> Python Console checked)

Any of the panels above can be turned on/off from menu View -> Panels.
Customizing the interface
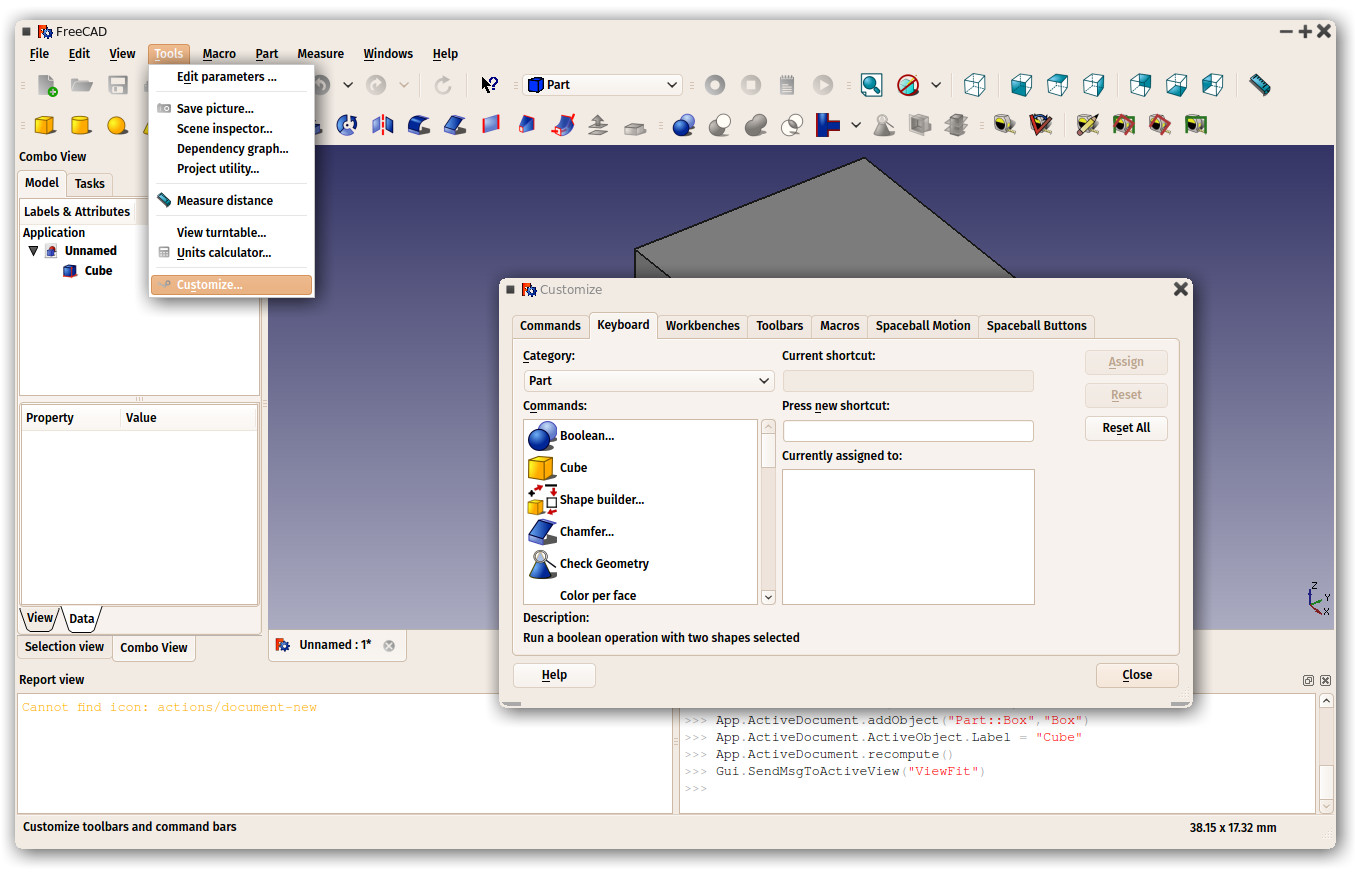
The interface of FreeCAD is deeply customizable. All panels and toolbars can be moved to different places or stacked one with another. They can also be closed and reopened when needed from the View menu or by right-clicking on an empty area of the interface. There are, however, many more options available, such as creating custom toolbars with tools from any of the Workbenches, or assigning and changing keyboard shortcuts.
These advanced customization options are availabe from the Tools -> Customize menu:
Read more
- Getting started with FreeCAD: http://www.freecadweb.org/wiki/index.php?title=Getting_started
- Customizing the interface: http://www.freecadweb.org/wiki/index.php?title=Interface_Customization
- Workbenches: http://www.freecadweb.org/wiki/index.php?title=Workbenches
- More about Python: https://www.python.org